Portal:Science
Science portal

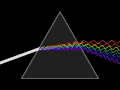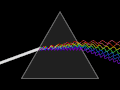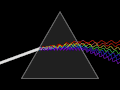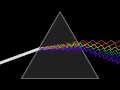
Science is a systematic discipline that builds and organises knowledge in the form of testable hypotheses and predictions about the world. Modern science is typically divided into two or three major branches: the natural sciences (e.g., physics, chemistry, and biology), which study the physical world; and the behavioural sciences (e.g., economics, psychology, and sociology), which study individuals and societies. The formal sciences (e.g., logic, mathematics, and theoretical computer science), which study formal systems governed by axioms and rules, are sometimes described as being sciences as well; however, they are often regarded as a separate field because they rely on deductive reasoning instead of the scientific method or empirical evidence as their main methodology. Applied sciences are disciplines that use scientific knowledge for practical purposes, such as engineering and medicine. (Full article...)
Featured article -
Abberton Reservoir is a pumped storage freshwater reservoir in eastern England near the Essex coast, with an area of 700 hectares (1,700 acres). Most of its water is pumped from the River Stour. It is the largest body of freshwater in Essex. (Full article...)
Banksia speciosa, commonly known as the showy banksia, is a species of large shrub or small tree in the family Proteaceae. It is found on the south coast of Western Australia between Hopetoun (34° S 120° E) and Point Culver (33° S 124° E), growing on white or grey sand in shrubland. Reaching up to 8 m (26 ft) in height, it is a single-stemmed plant that has thin leaves with prominent triangular 'teeth' along each margin, which are 20–45 cm (7.9–17.7 in) long and 2–4 cm (0.8–1.6 in) wide. The prominent cream-yellow flower spikes known as inflorescences appear throughout the year. As they age they develop up to 20 follicles each that store seeds until opened by fire. Though widely occurring, the species is highly sensitive to dieback and large populations of plants have succumbed to the disease. (Full article...)

The golden-crowned sifaka or Tattersall's sifaka (Propithecus tattersalli) is a medium-sized lemur characterized by mostly white fur, prominent furry ears, and a golden-orange crown. It is one of the smallest sifakas (genus Propithecus), weighing around 3.5 kg (7.7 lb) and measuring approximately 90 cm (35 in) from head to tail. Like all sifakas, it is a vertical clinger and leaper, and its diet includes mostly seeds and leaves. The golden-crowned sifaka is named after its discoverer, Ian Tattersall, who first spotted the species in 1974. However, it was not formally described until 1988, after a research team led by Elwyn L. Simons observed and captured some specimens for captive breeding. The golden-crowned sifaka most closely resembles the western forest sifakas of the P. verreauxi group, yet its karyotype suggests a closer relationship with the P. diadema group of eastern forest sifakas. Despite the similarities with both groups, more recent studies of its karyotype support its classification as a distinct species. (Full article...)
The rock martin (Ptyonoprogne fuligula) is a small passerine bird in the swallow family that is resident in central and southern Africa. It breeds mainly in the mountains, but also at lower altitudes, especially in rocky areas and around towns, and, unlike most swallows, it is often found far from water. It is 12–15 cm (4.7–5.9 in) long, with mainly brown plumage, paler-toned on the upper breast and underwing coverts, and with white "windows" on the spread tail in flight. The sexes are similar in appearance, but juveniles have pale fringes to the upperparts and flight feathers. The former northern subspecies are smaller, paler, and whiter-throated than southern African forms, and are now usually split as a separate species, the pale crag martin. The rock martin hunts along cliff faces for flying insects using a slow flight with much gliding. Its call is a soft twitter. (Full article...)
Mauna Kea (/ˌmɔːnə ˈkeɪə, ˌmaʊnə -/, Hawaiian: [ˈmɐwnə ˈkɛjə]; abbreviation for Mauna a Wākea) is a dormant shield volcano on the island of Hawaiʻi. Its peak is 4,207.3 m (13,803 ft) above sea level, making it the highest point in Hawaii and the island with the second highest high point, behind New Guinea, the world's largest tropical island with multiple peaks that are higher. The peak is about 38 m (125 ft) higher than Mauna Loa, its more massive neighbor. Mauna Kea is unusually topographically prominent for its height: its prominence from sea level is fifteenth in the world among mountains, at 4,207.3 m (13,803 ft); its prominence from under the ocean is 9,330 m (30,610 ft), rivaled only by Mount Everest. This dry prominence is greater than Everest's height above sea level of 8,848.86 m (29,032 ft), and some authorities have labeled Mauna Kea the tallest mountain in the world, from its underwater base. Mauna Kea is ranked 8th by topographic isolation. (Full article...)
The white-headed fruit dove (Ptilinopus eugeniae) is a species of bird in the pigeon family Columbidae. It was described by the English ornithologist John Gould in 1856, and the specific name eugeniae honours the French empress Eugénie de Montijo. Adults of the species have white heads, a purplish-red breast patch, a grey shoulder patch, olive-green upperparts, greenish underparts with a blue tinge, and a yellowish vent. Juveniles have green heads with the white restricted to the forehead and upper throat, a much smaller grey shoulder patch, and the red breast patch restricted to the centre of the breast. (Full article...)
Mayflies (also known as shadflies or fishflies in Canada and the upper Midwestern United States, as Canadian soldiers in the American Great Lakes region, and as up-winged flies in the United Kingdom) are aquatic insects belonging to the order Ephemeroptera. This order is part of an ancient group of insects termed the Palaeoptera, which also contains dragonflies and damselflies. Over 3,000 species of mayfly are known worldwide, grouped into over 400 genera in 42 families. (Full article...)
Featured pictures
Vital articles

Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary information encoded in genes, which can be transmitted to future generations. Another major theme is evolution, which explains the unity and diversity of life. Energy processing is also important to life as it allows organisms to move, grow, and reproduce. Finally, all organisms are able to regulate their own internal environments. (Full article...)
Did you know...
- ... that Guy Parmelin, now President of Switzerland, opened the study program of cyber security of the Lucerne School of Information Technology in 2018?
- ... that Margareth Rago seeks to establish a methodology for what she calls "feminist science"?
- ... that public health measures and advances in medical science in modern human history helped raise global life expectancy from about 31 years in 1900 to over 66 years in 2000?
- ... that Charles Leslie Richardson was ordered to "make science fashionable in the army"?
- ... that the science-fiction video game The Anacrusis is named after a musical term?
- ... that characters from several different science fiction media appear as an Easter egg in the episode "Babylon's Ashes"?
Get involved
| This portal needs to be updated. Please help update this portal to reflect recent events or newly available information. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. |

|
|
Science News
- 24 September 2024 –
- Scientists from the University of Waterloo announce that they have positively identified bones found on King William Island in Nunavut, Canada, as those of James Fitzjames, captain of HMS Erebus during Franklin's lost expedition. (CBC News)
- 23 September 2024 – Deforestation of the Amazon rainforest
- Climate researchers report that since 1985, deforestation in the Amazon has caused the loss of an area of rainforest equal to the combined area of France and Germany. (France 24)
- 22 September 2024 –
- Researchers from the University of Cape Town and the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology announce they have reconstructed the oldest human genome ever found, belonging to a man and a woman who lived about 10,000 years ago in the Mesolithic period. The prior oldest decoded genome was from about 2,000 years ago. (DW)
- 15 September 2024 – Polaris program
- The spacecraft of the Polaris Dawn private spaceflight mission operated by SpaceX returns to Earth after five days in orbit. (BBC News)
- 12 September 2024 – Polaris program
- American billionaire Jared Isaacman becomes the first person to perform a commercial spacewalk as part of the Polaris Dawn private spaceflight mission operated by SpaceX. (AP)
- 11 September 2024 – Spaceflight
- Following the launch of the Russian Soyuz MS-26 spacecraft from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan, there were a record 19 people in outer space: the three astronauts on the MS-26 mission, three more on China's Tiangong space station, four people on the SpaceX Polaris Dawn mission, and nine more on board the International Space Station. (CollectSPACE)