Portal:Mathematics
The Mathematics Portal
Mathematics is the study of representing and reasoning about abstract objects (such as numbers, points, spaces, sets, structures, and games). Mathematics is used throughout the world as an essential tool in many fields, including natural science, engineering, medicine, and the social sciences. Applied mathematics, the branch of mathematics concerned with application of mathematical knowledge to other fields, inspires and makes use of new mathematical discoveries and sometimes leads to the development of entirely new mathematical disciplines, such as statistics and game theory. Mathematicians also engage in pure mathematics, or mathematics for its own sake, without having any application in mind. There is no clear line separating pure and applied mathematics, and practical applications for what began as pure mathematics are often discovered. (Full article...)
Featured articles –
Selected image –
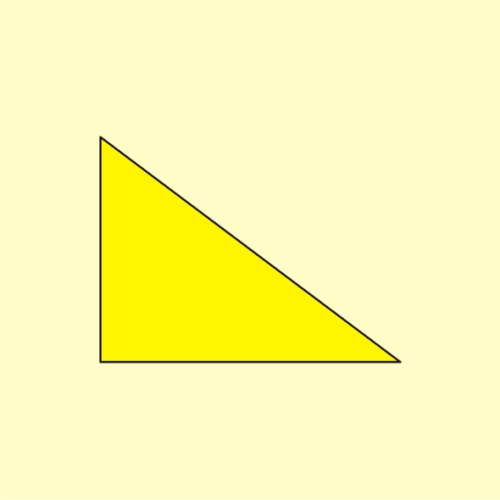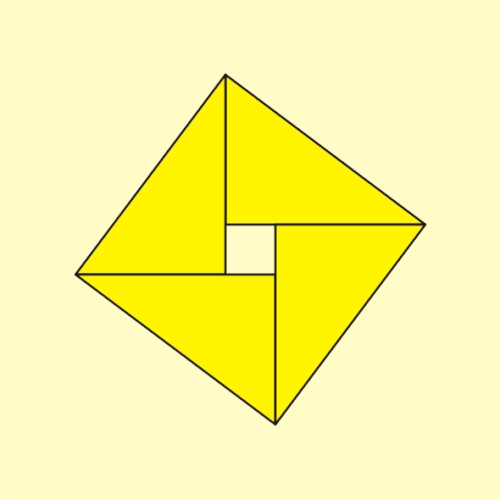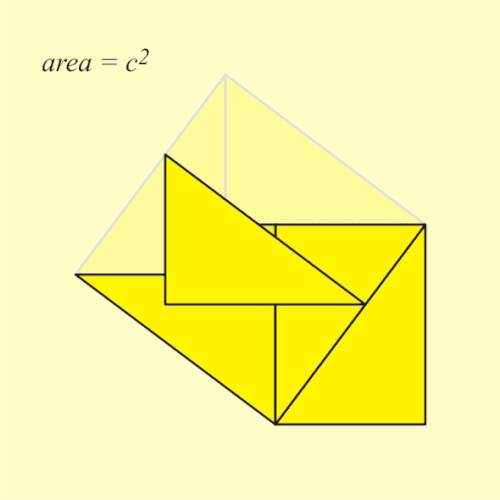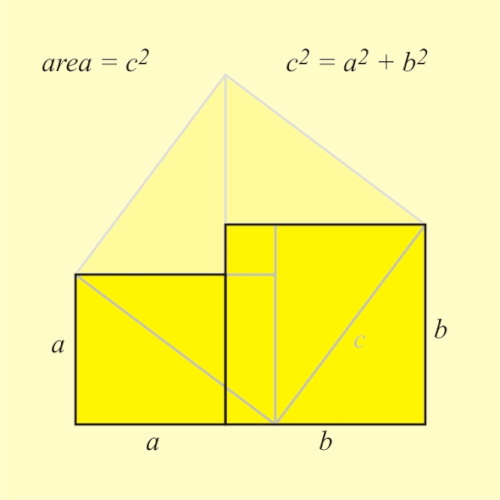
Good articles –
Did you know (auto-generated) –

- ... that the British National Hospital Service Reserve trained volunteers to carry out first aid in the aftermath of a nuclear or chemical attack?
- ... that in 1940 Xu Ruiyun became the first Chinese woman to receive a PhD in mathematics?
- ... that mathematician Daniel Larsen was the youngest contributor to the New York Times crossword puzzle?
- ... that Fathimath Dheema Ali is the first Olympic qualifier from the Maldives?
- ... that the word algebra is derived from an Arabic term for the surgical treatment of bonesetting?
- ... that the prologue to The Polymath was written by Martin Kemp, a leading expert on Leonardo da Vinci?
- ... that Ukrainian baritone Danylo Matviienko, who holds a master's degree in mathematics, appeared as Demetrius in Britten's opera A Midsummer Night's Dream at the Oper Frankfurt?
- ... that although the problem of squaring the circle with compass and straightedge goes back to Greek mathematics, it was not proven impossible until 1882?
More did you know –

- ...the Piphilology record (memorizing digits of Pi) is 70000 as of Mar 2015?
- ...that people are significantly slower to identify the parity of zero than other whole numbers, regardless of age, language spoken, or whether the symbol or word for zero is used?
- ...that Auction theory was successfully used in 1994 to sell FCC airwave spectrum, in a financial application of game theory?
- ...properties of Pascal's triangle have application in many fields of mathematics including combinatorics, algebra, calculus and geometry?
- ...work in artificial intelligence makes use of swarm intelligence, which has foundations in the behavioral examples found in nature of ants, birds, bees, and fish among others?
- ...that statistical properties dictated by Benford's Law are used in auditing of financial accounts as one means of detecting fraud?
- ...that modular arithmetic has application in at least ten different fields of study, including the arts, computer science, and chemistry in addition to mathematics?
Selected article –
 |
| A dodecahedron, one of the five Platonic solids Image credit: User:DTR |
A regular polytope is a geometric figure with a high degree of symmetry. Examples in two dimensions include the square, the regular pentagon and hexagon, and so on. In three dimensions the regular polytopes include the cube, the dodecahedron, and all other Platonic solids. Other Platonic solids include the tetrahedron, the octahedron, the icosahedron. Examples exist in higher dimensions also, such as the 5-dimensional hendecatope. Circles and spheres, although highly symmetric, are not considered polytopes because they do not have flat faces. The strong symmetry of the regular polytopes gives them an aesthetic quality that interests both non-mathematicians and mathematicians.
Many regular polytopes, at least in two and three dimensions, exist in nature and have been known since prehistory. The earliest surviving mathematical treatment of these objects comes to us from ancient Greek mathematicians such as Euclid. Indeed, Euclid wrote a systematic study of mathematics, publishing it under the title Elements, which built up a logical theory of geometry and number theory. His work concluded with mathematical descriptions of the five Platonic solids. (Full article...)
| View all selected articles |
Subcategories

Algebra | Arithmetic | Analysis | Complex analysis | Applied mathematics | Calculus | Category theory | Chaos theory | Combinatorics | Dynamical systems | Fractals | Game theory | Geometry | Algebraic geometry | Graph theory | Group theory | Linear algebra | Mathematical logic | Model theory | Multi-dimensional geometry | Number theory | Numerical analysis | Optimization | Order theory | Probability and statistics | Set theory | Statistics | Topology | Algebraic topology | Trigonometry | Linear programming
Mathematics | History of mathematics | Mathematicians | Awards | Education | Literature | Notation | Organizations | Theorems | Proofs | Unsolved problems
Topics in mathematics
| General | Foundations | Number theory | Discrete mathematics |
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
| Algebra | Analysis | Geometry and topology | Applied mathematics |
Index of mathematics articles
| ARTICLE INDEX: | |
| MATHEMATICIANS: |
Related portals
WikiProjects
![]() The Mathematics WikiProject is the center for mathematics-related editing on Wikipedia. Join the discussion on the project's talk page.
The Mathematics WikiProject is the center for mathematics-related editing on Wikipedia. Join the discussion on the project's talk page.
In other Wikimedia projects
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus